Hollins Homes supported the planting of 2 hecatres of wildflowers in the UK in 2023-24
Hollins Homes is part of an imaginative and beautiful solution to the problem of the loss of flowers and pollinators in the UK. Not only are wildflowers attractive and beneficial to our well-being, but for the thousands of pollinating insects, wildflowers are critical.
Since 1940 we’ve lost ninety seven percent of our flower rich meadows and hundreds of our pollinator species are in decline. In areas, our local wildlife finds itself in isolated oases, walled in by agricultural land, urban landscapes, roads, and gardens.
Our solution is to restore B-Lines – a network of insect pathways along which we are restoring and creating wildflower rich habitat. These insect super highways created in partnership with GreenTheUK and Buglife will extend across the whole of the UK, allowing wildlife to move freely through our countryside and towns. Thanks to Hollins Homes, we have created a network of flower-rich pathways benefitting pollinators, other wildlife and people.
Hollins Homes has supported the planting of 2 hectares of wildflowers. The second hectare is to follow and will be restored in 2024.
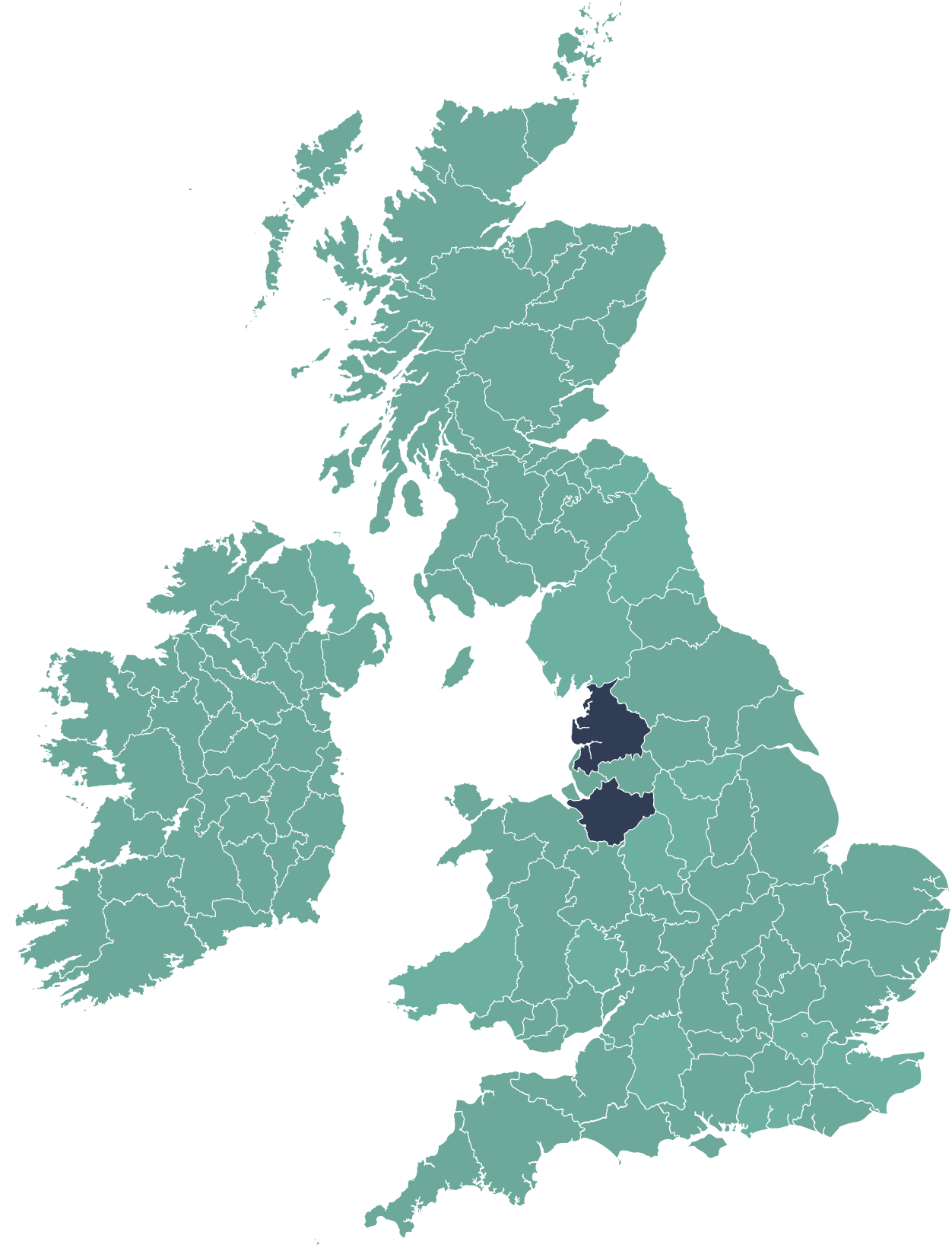
Wildflower Restoration in Cheshire (1 hectare)
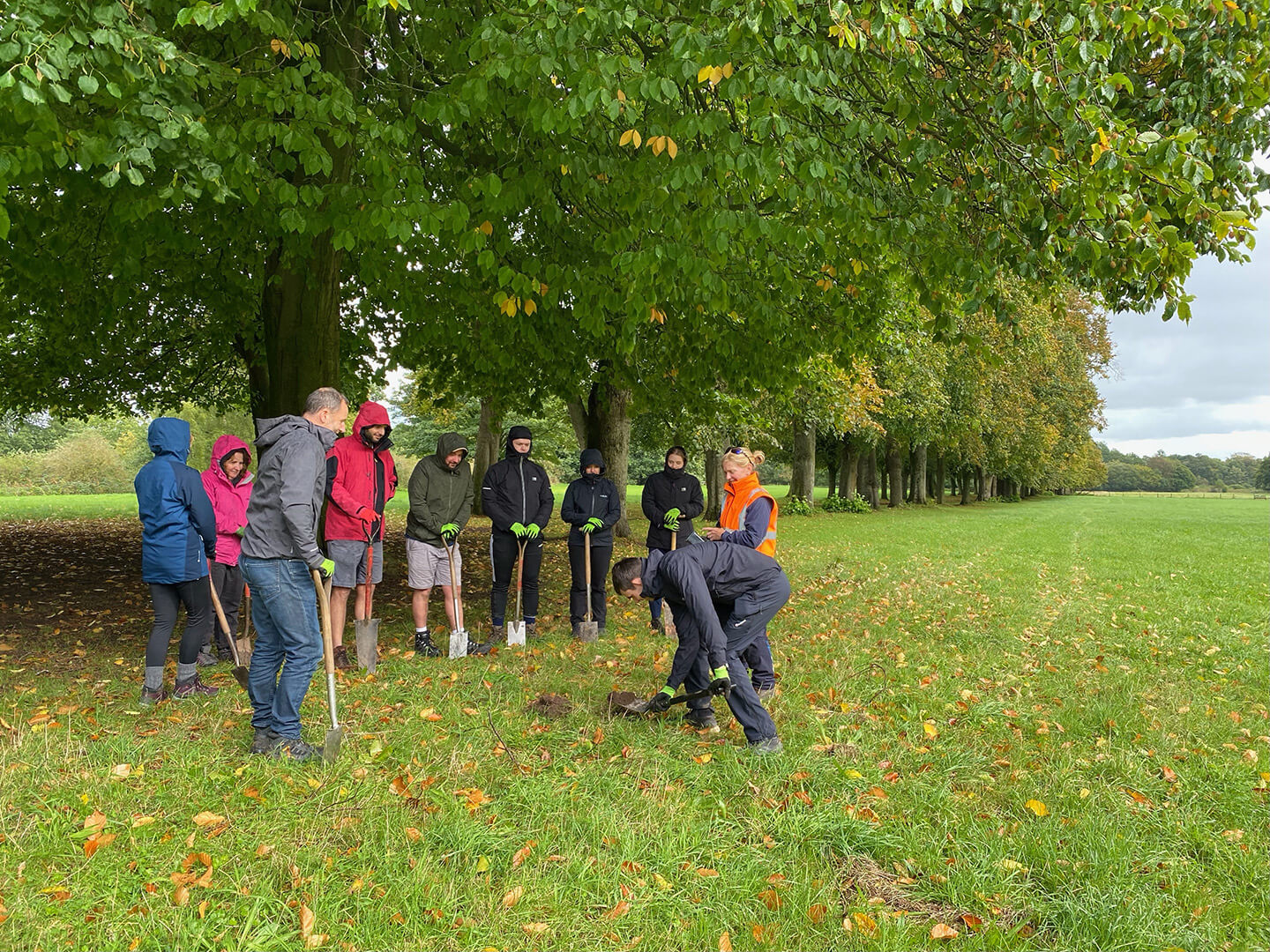
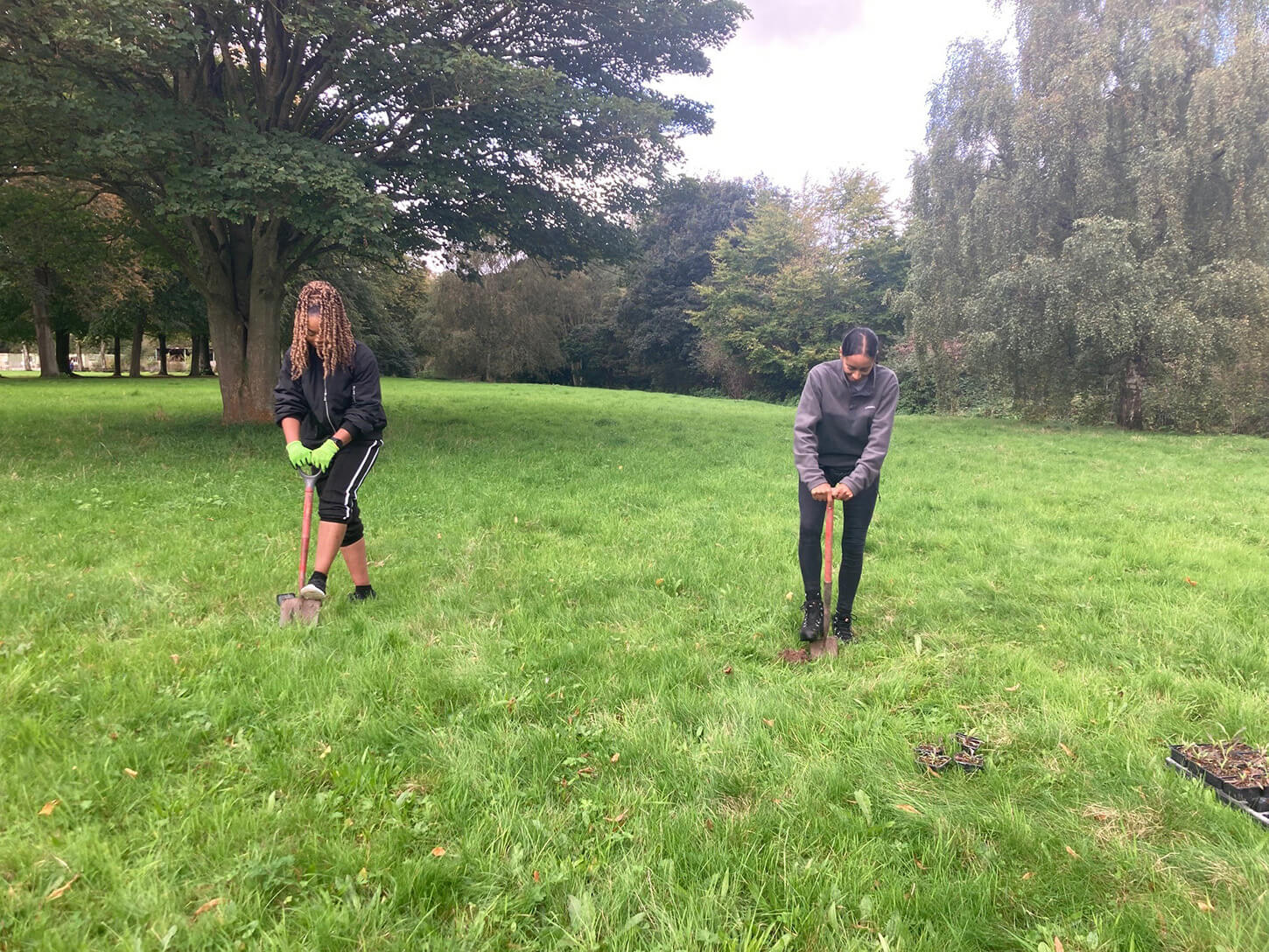
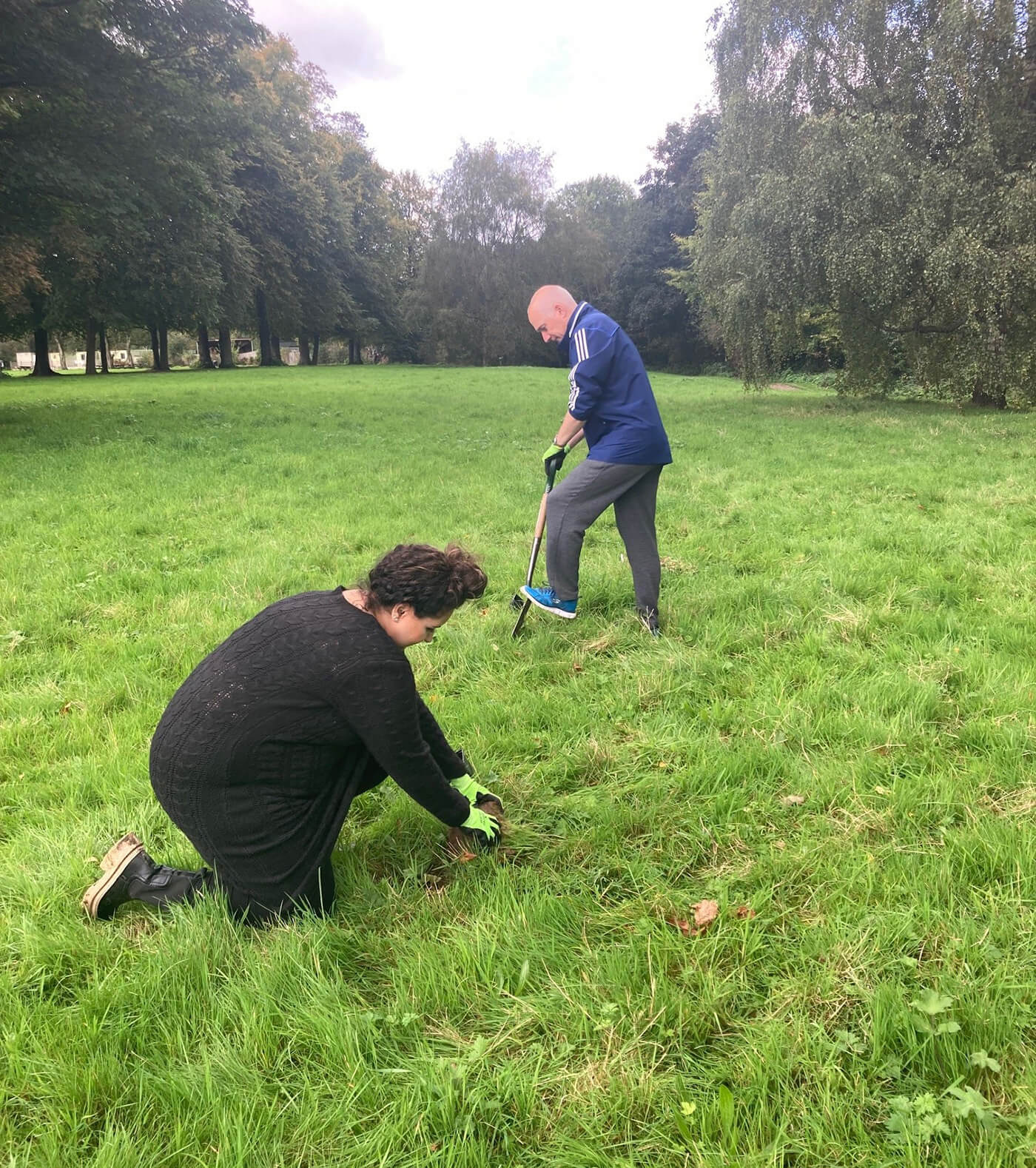
Marbury Country Park lies in the heart of the Northwich Community Woodlands, where what was once former industrial land is gradually being transformed to create a rich and green environment stretching from Northwich to Marbury. The woods sit within 350 hectares of parkland and are home to many endangered species such as Bitterns. Hollins Homes sponsored the restoration and enhancement of local wildflower meadows with the planting of wildflower plugs across existing meadows.
Hollins Homes is further supporting the B-lines network by restoring another hectare of wildflowers in 2024 in a priority location that will benefit local biodiversity. More details will follow post planting.
Wildflower Restoration in Lancashire (1 hectare)
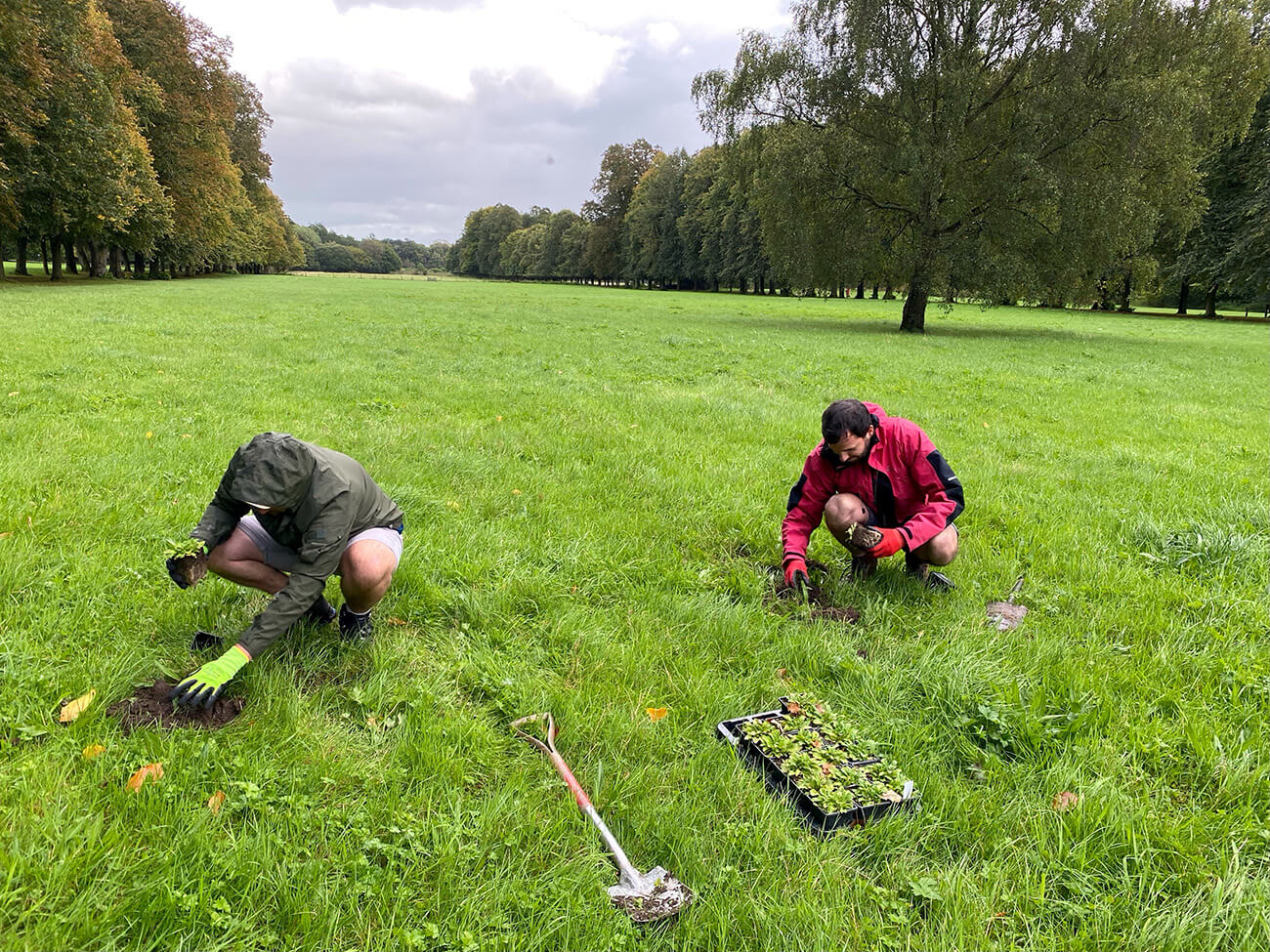
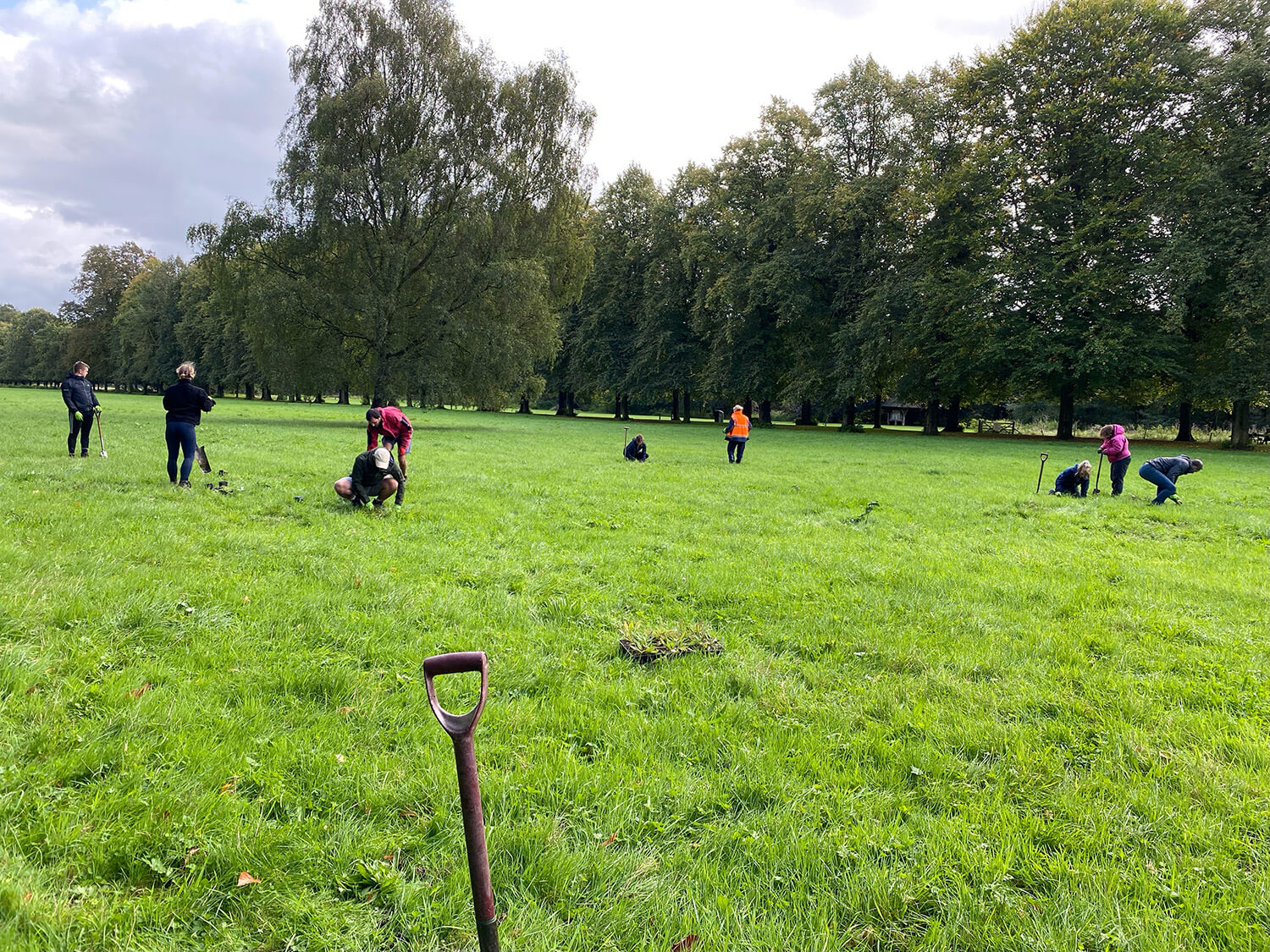
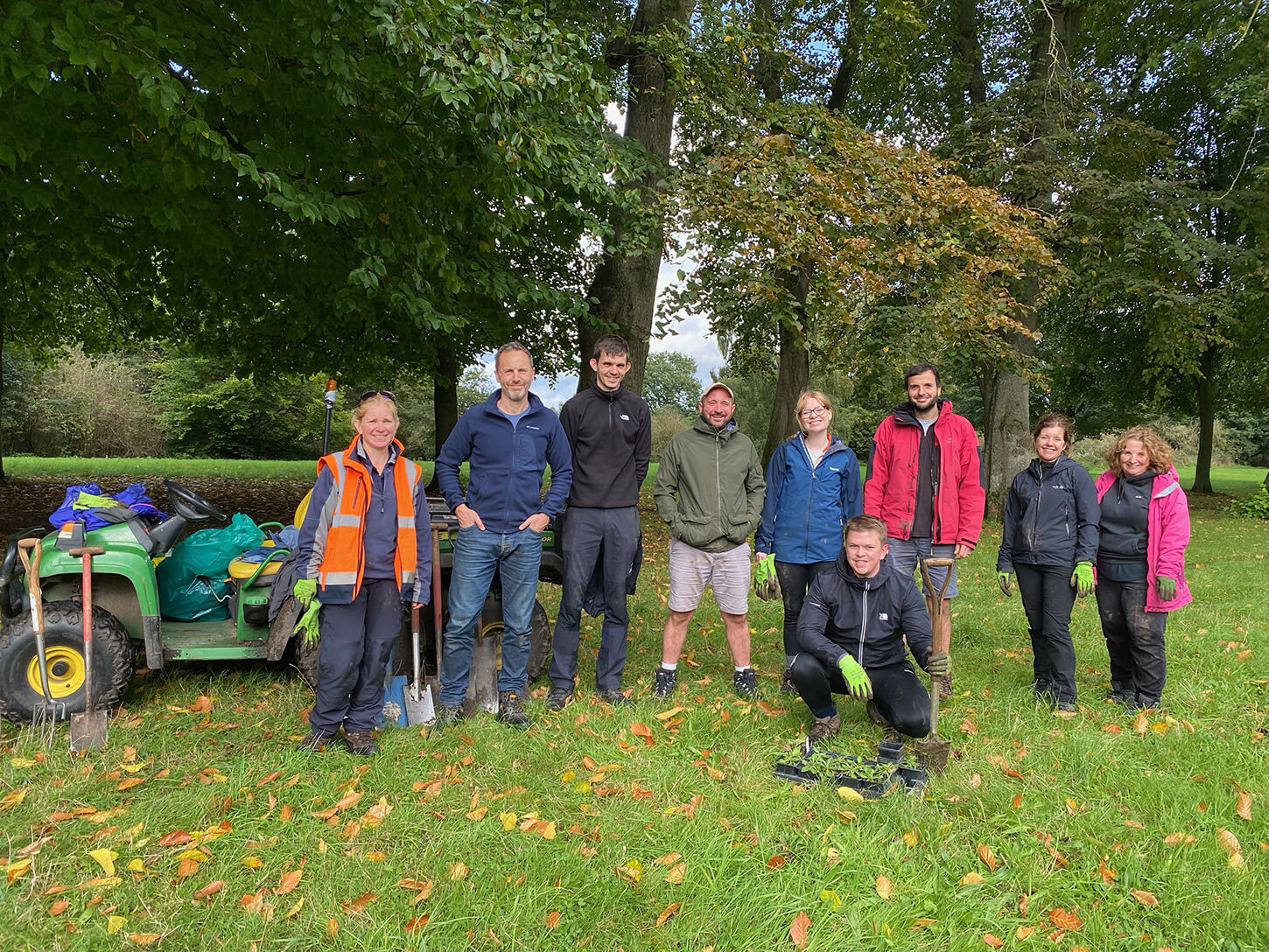
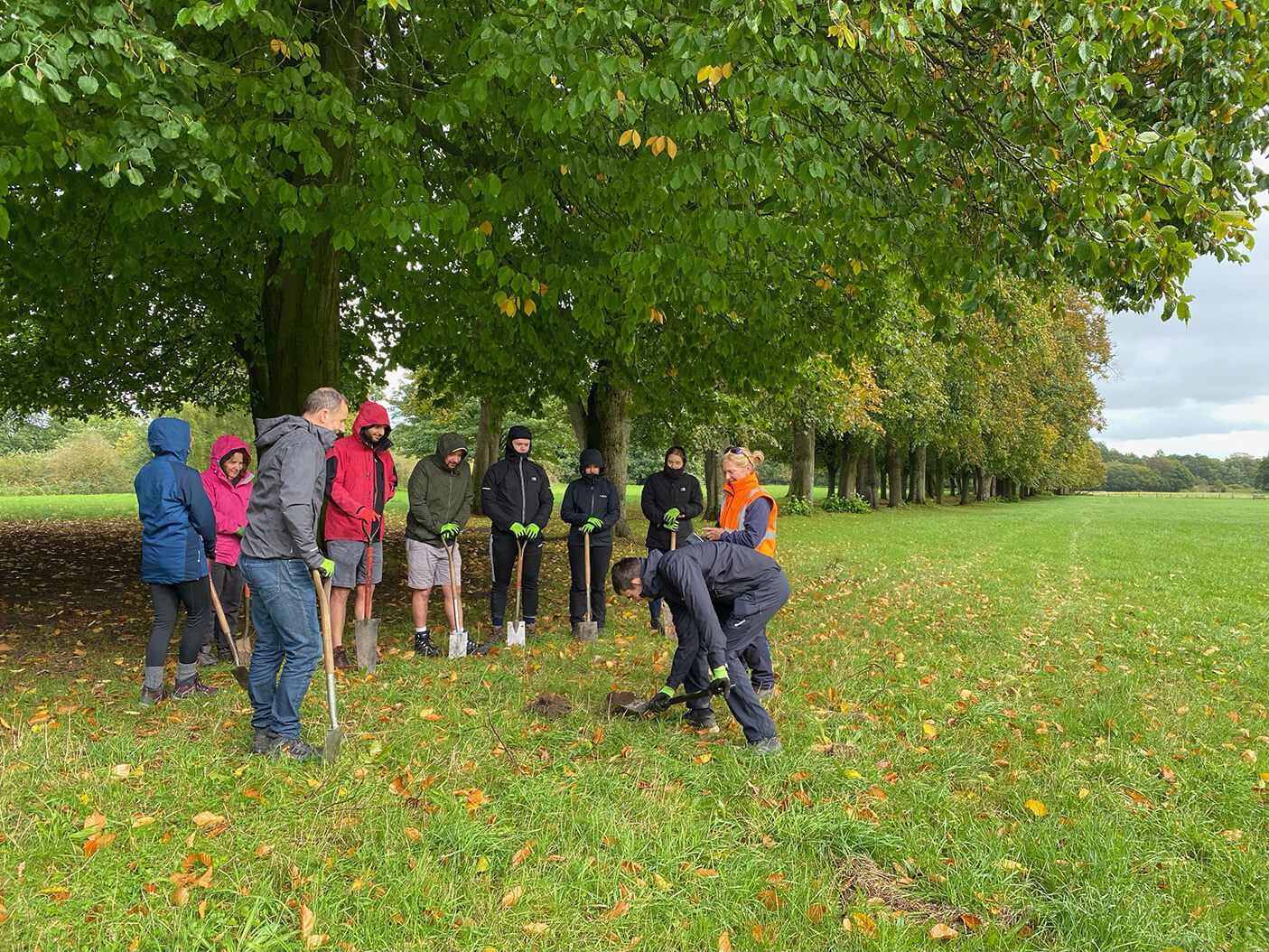
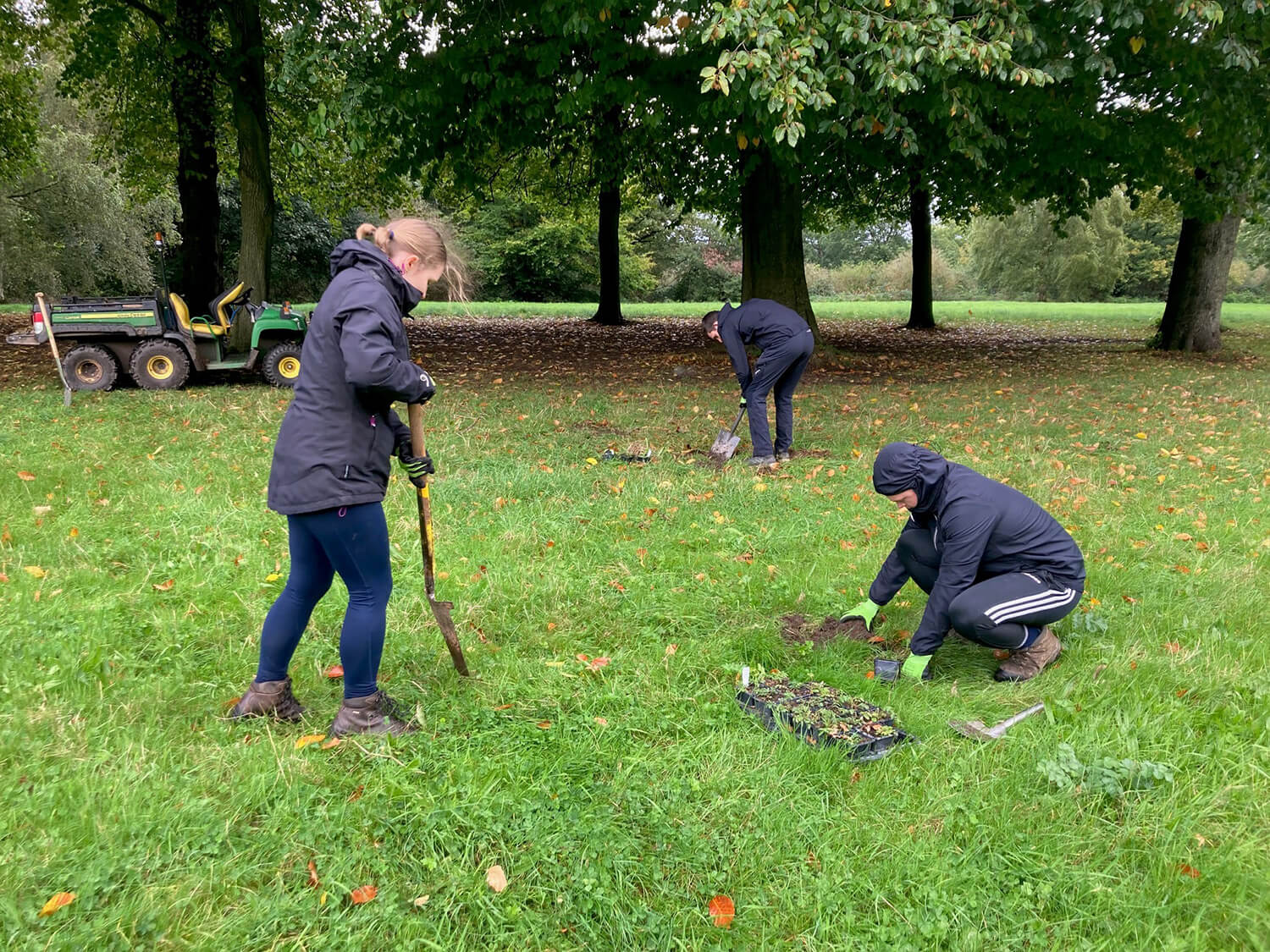
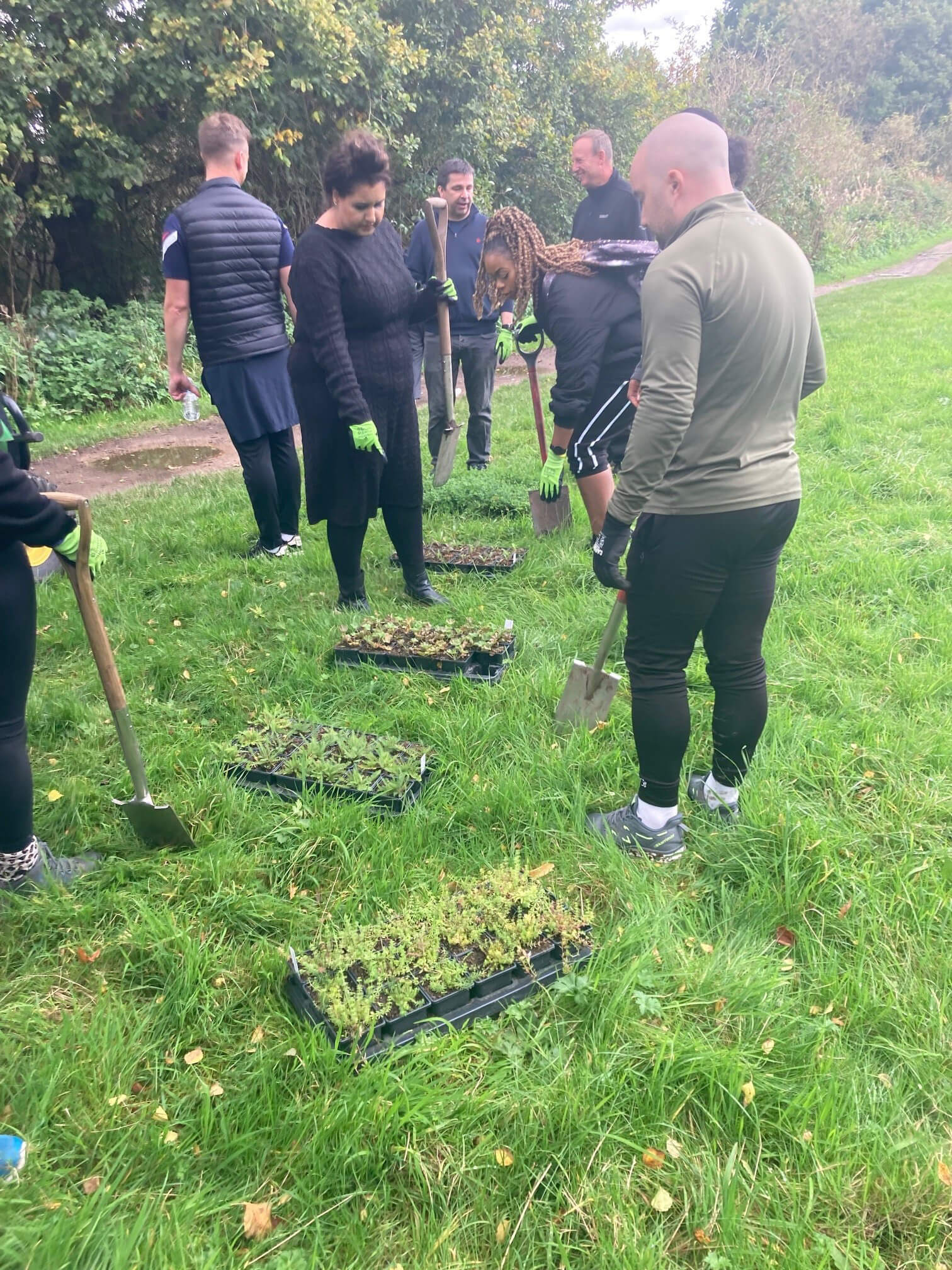
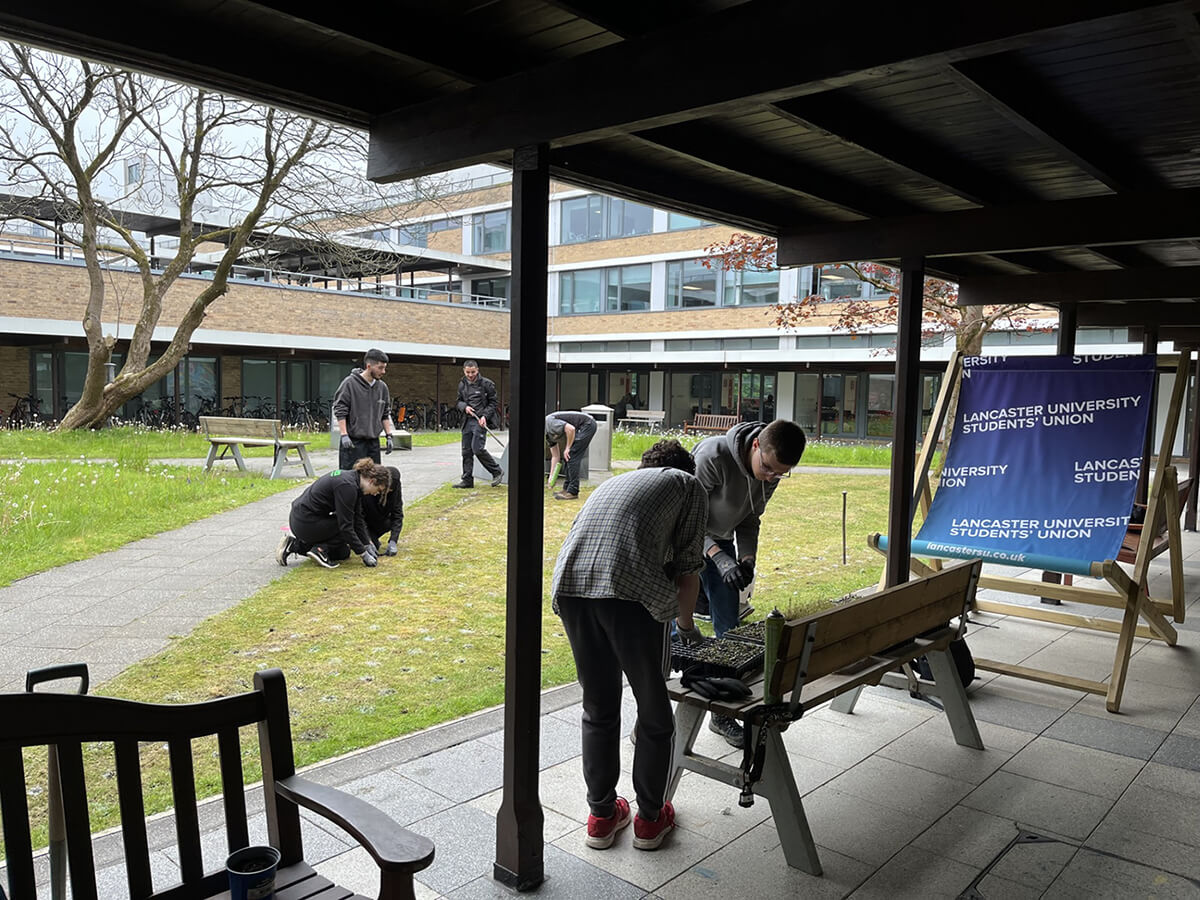
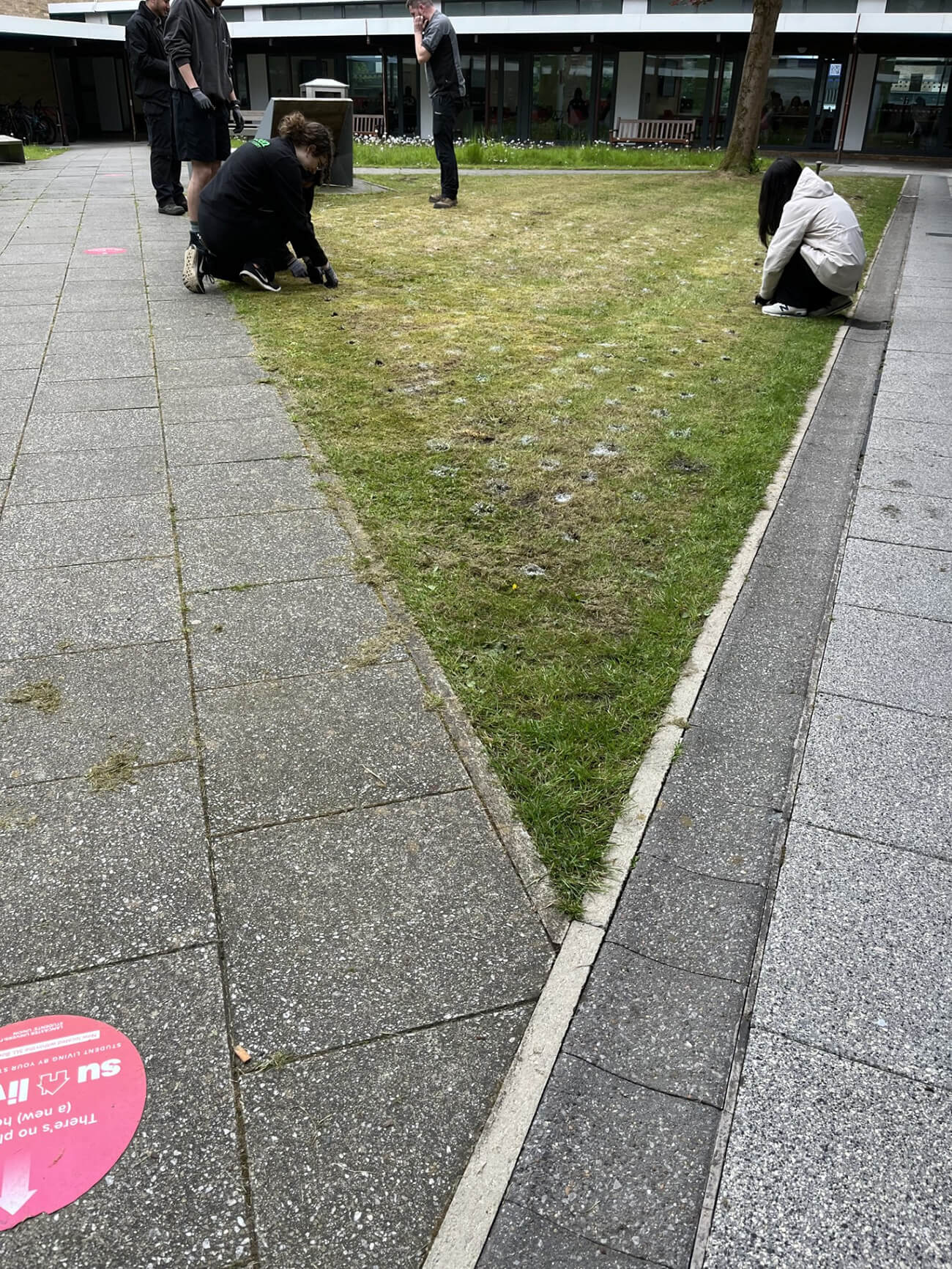
Hollins Homes supported wildflower planting in Lancashire at the University of Lancaster. 11 students from the Student Union's Green Lancaster took part in the planting with the Grounds team within one of the College's outdoor spaces to enhance existing and ongoing wildflower meadow projects on site. The planting area links well with other areas of grassland that the university are developing into a meadow and a mixture of species were chosen for the local habitat, including Yellow Rattle, Oxeye Daisy and Common Knapweed, amongst others. The Yellow Rattle was specifically chosen to supresses existing grasses across university meadows, allowing newer wildflowers to grow through.
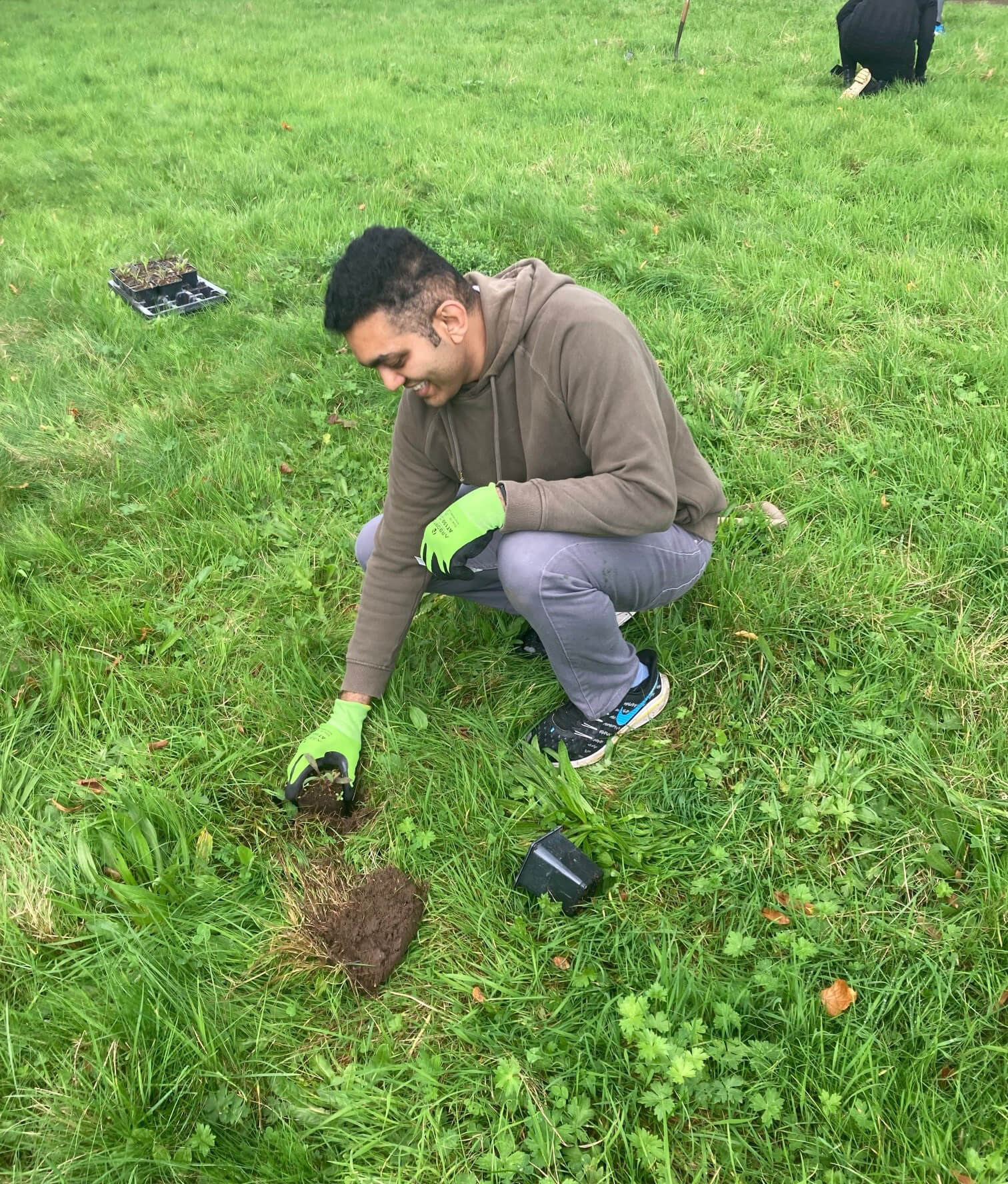
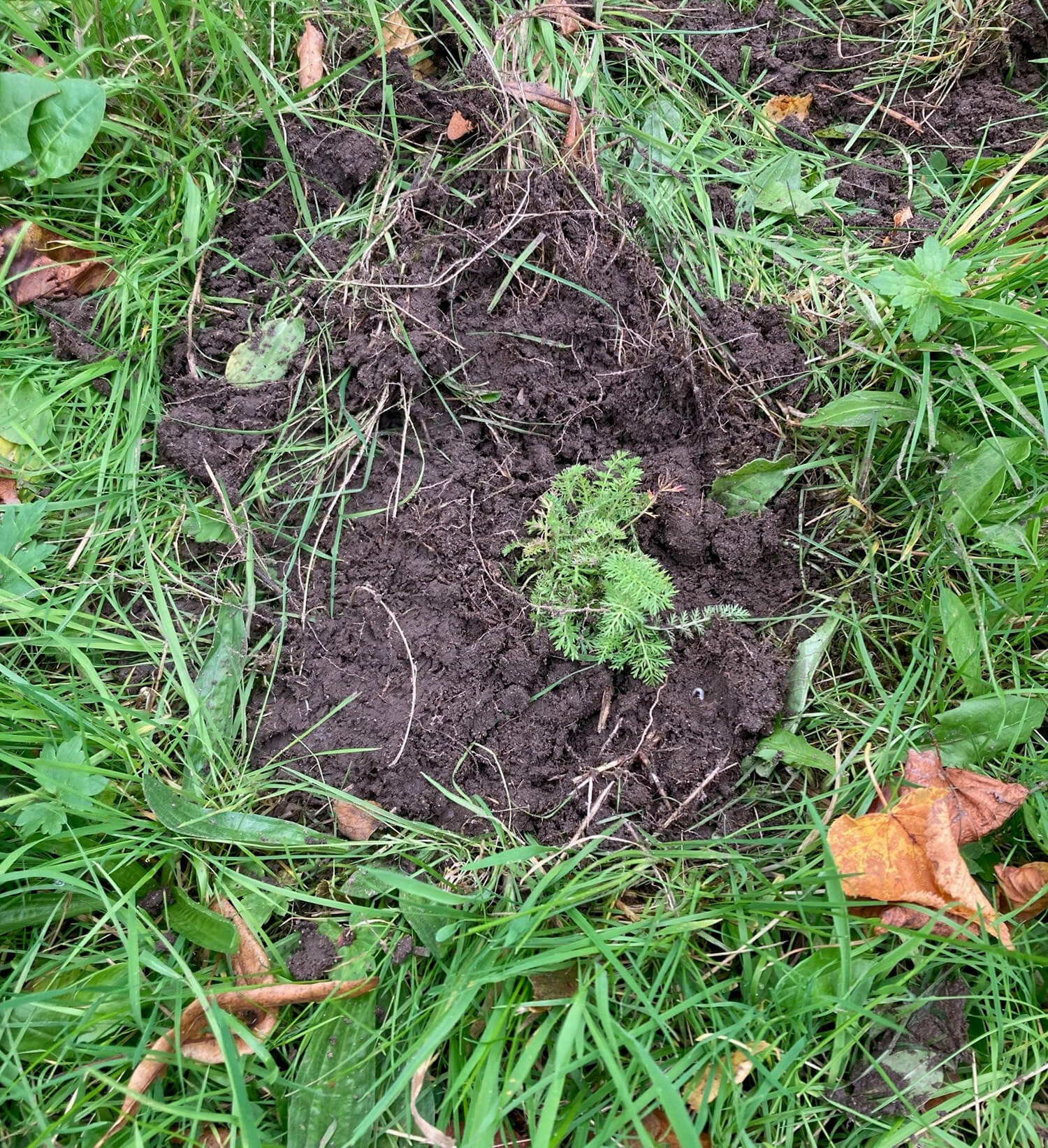
Plug planting is a great way to add extra species to a site and give them a better chance of establishing. We often supplement seed scattering with additional plug plants to either add certain species that may not have been included in the seed mixes or bolster the site with specific species suited to the habitat. Plug plants often have a higher survival rate and prove more effective in the long run when trying to make sure certain species are present on a given site. They act similarly to when you plant potted plants in your garden or window box, providing an instant source of habitat, shelter, and food (when in flower) for local pollinating insects and other invertebrates. They also provide volunteers with a rewarding exercise so you are able to immediately see the impact of your planting on a site.
Wildflowers & Grasses Planted
UN's Sustainable Development Goals
As a GreenTheUK partner, you support projects that are in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.

Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.

Sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity loss.






































































