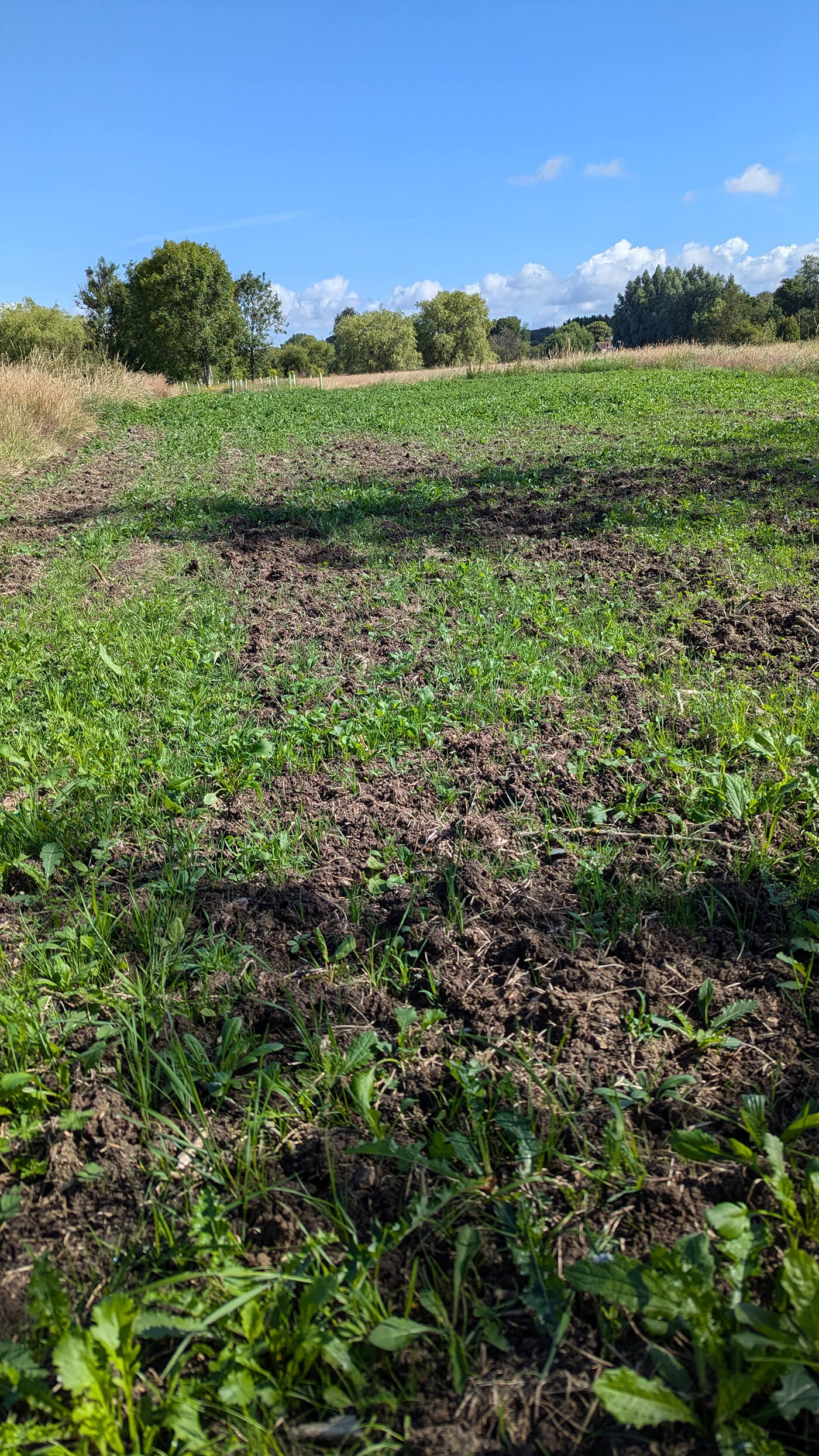
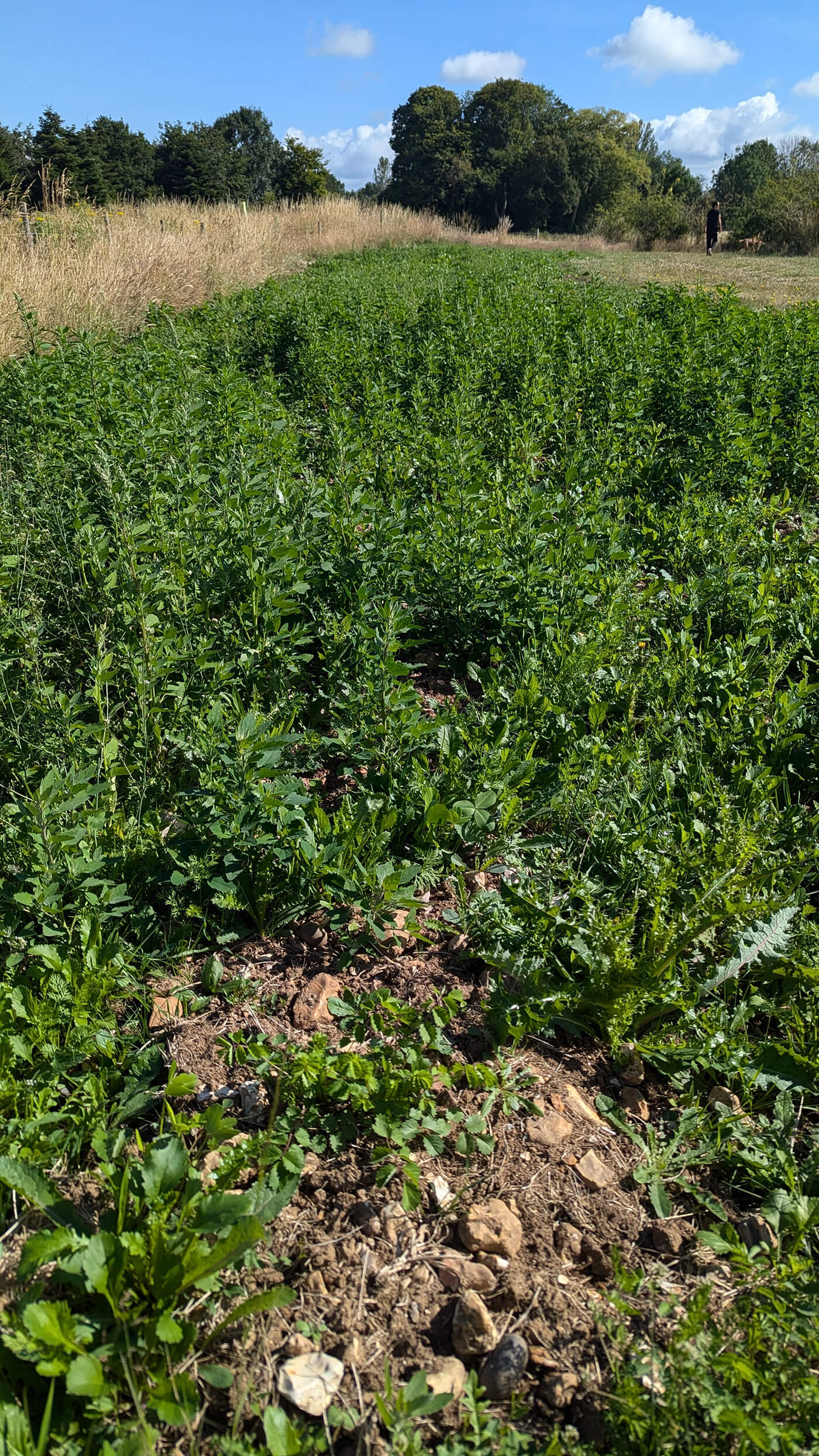
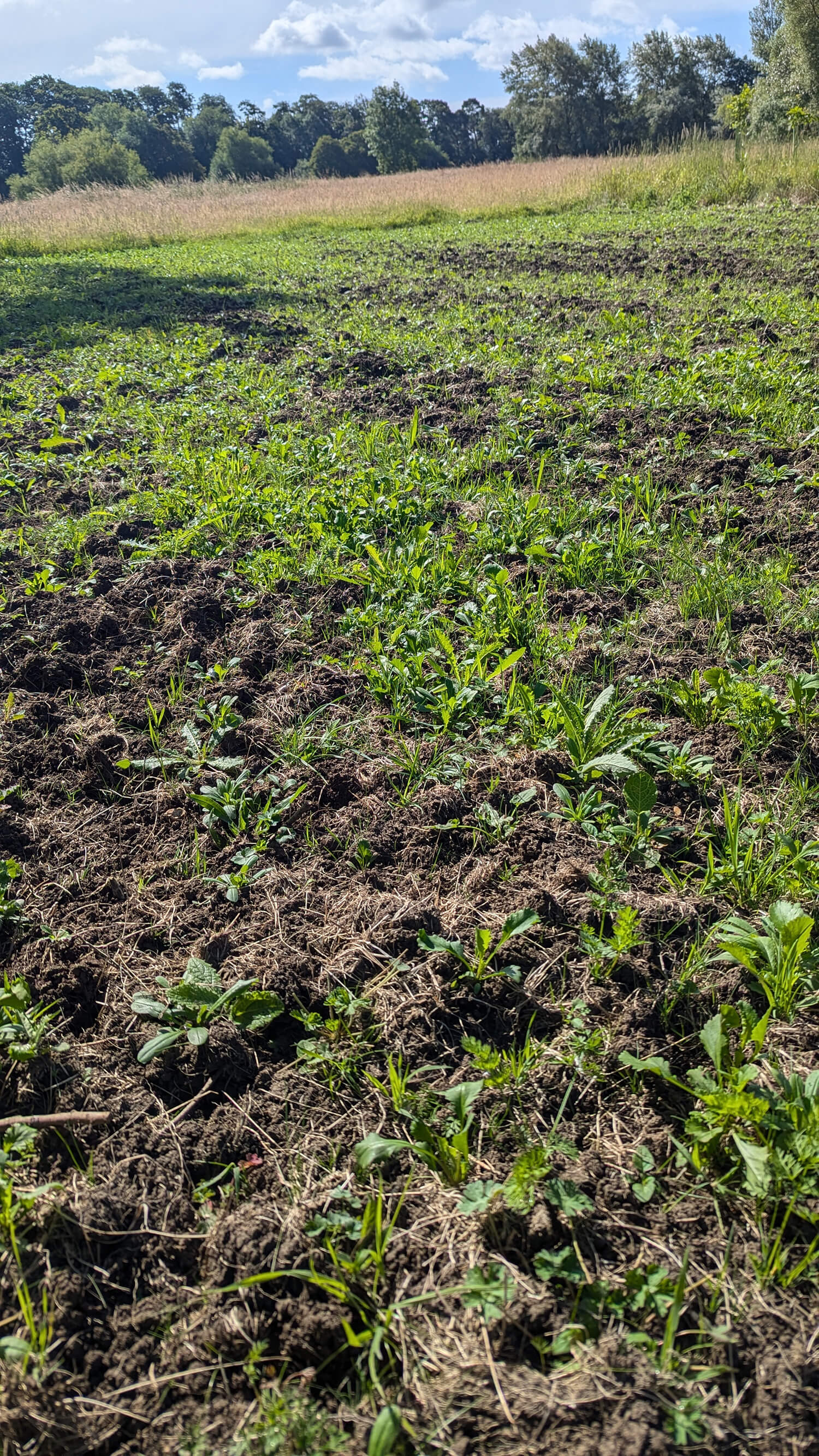
Outpost VFX supported the planting of 2 hectares of wildflowers in the UK across 2023-2024
Outpost VFX is part of an imaginative and beautiful solution to the problem of the loss of flowers and pollinators in the UK. Not only are wildflowers attractive and beneficial to our well-being, but for the thousands of pollinating insects, wildflowers are critical.
Since 1940 we’ve lost ninety seven percent of our flower rich meadows and hundreds of our pollinator species are in decline. In areas, our local wildlife finds itself in isolated oases, walled in by agricultural land, urban landscapes, roads, and gardens.
Our solution is to restore B-Lines – a network of insect pathways along which we are restoring and creating wildflower rich habitat. These insect super highways created in partnership with GreenTheUK and Buglife will extend across the whole of the UK, allowing wildlife to move freely through our countryside and towns. Thanks to support from Outpost VFX, a network of flower-rich pathways that benefits pollinators, other wildlife and people has been created.

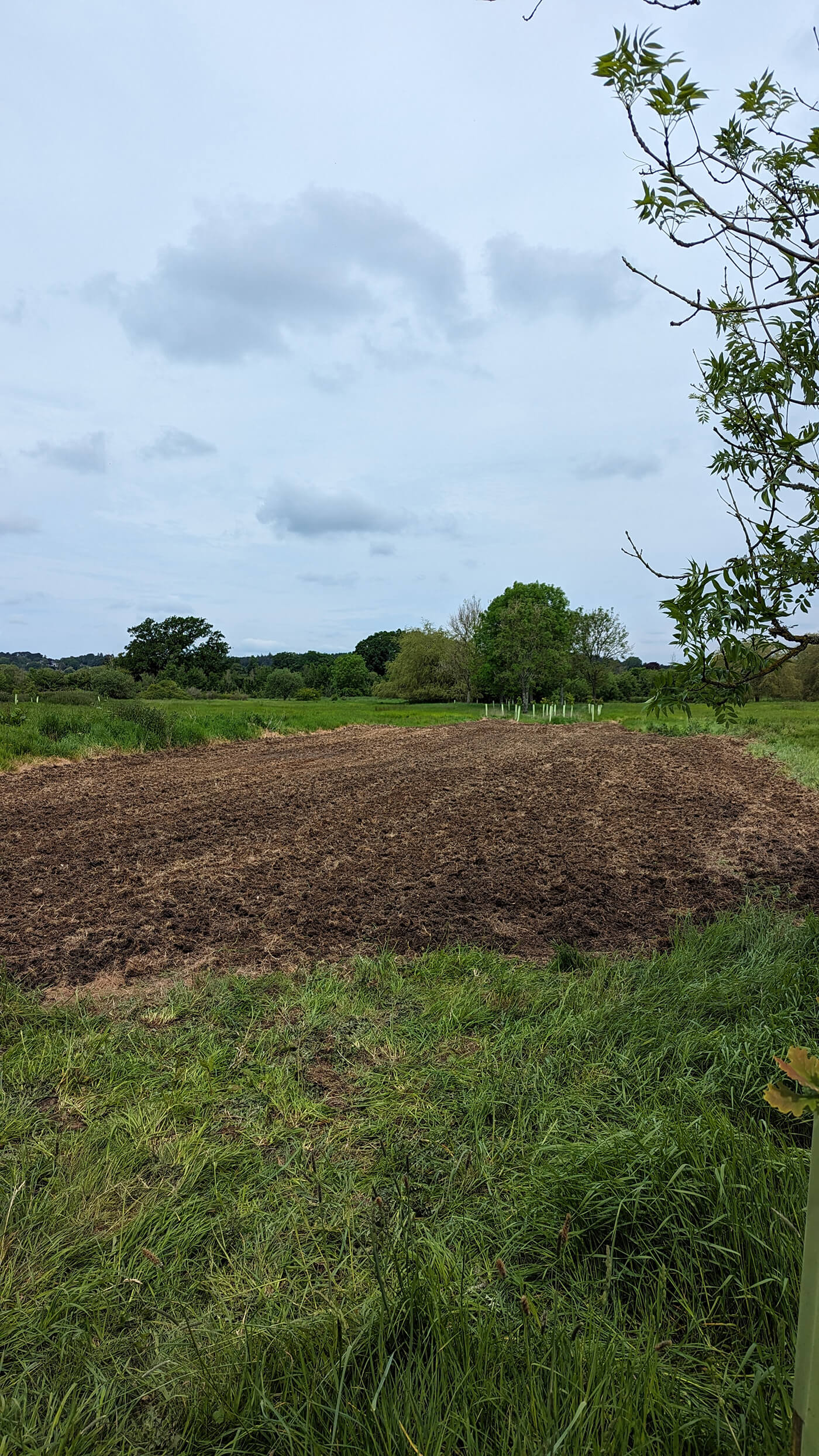
Wildflower Restoration in Hampshire (2 hectares)
Outpost VFX has supported the planting of native wildflowers at Canford Park, a Suitable Alternative Natural Greenspace (SANG) located just north of the city. A SANG is similar to a country park albeit with a particular purpose: to reduce recreational pressure on sensitive habitats and protect the species therein.
The Dorset Heathlands are of European nature conservation importance and designated as a Special Protection Area. Restoration work at Canford Park complements the work happening in Poole and Bournemouth to conserve species and regenerate green spaces that are considered vulnerable and sensitive to additional development pressures.
Natural England outlines various guidlines for the creation of SANG sites including: a variety of habitats, a network of public footpaths and desirable features such as areas of dense trees, scattered scub or open water.
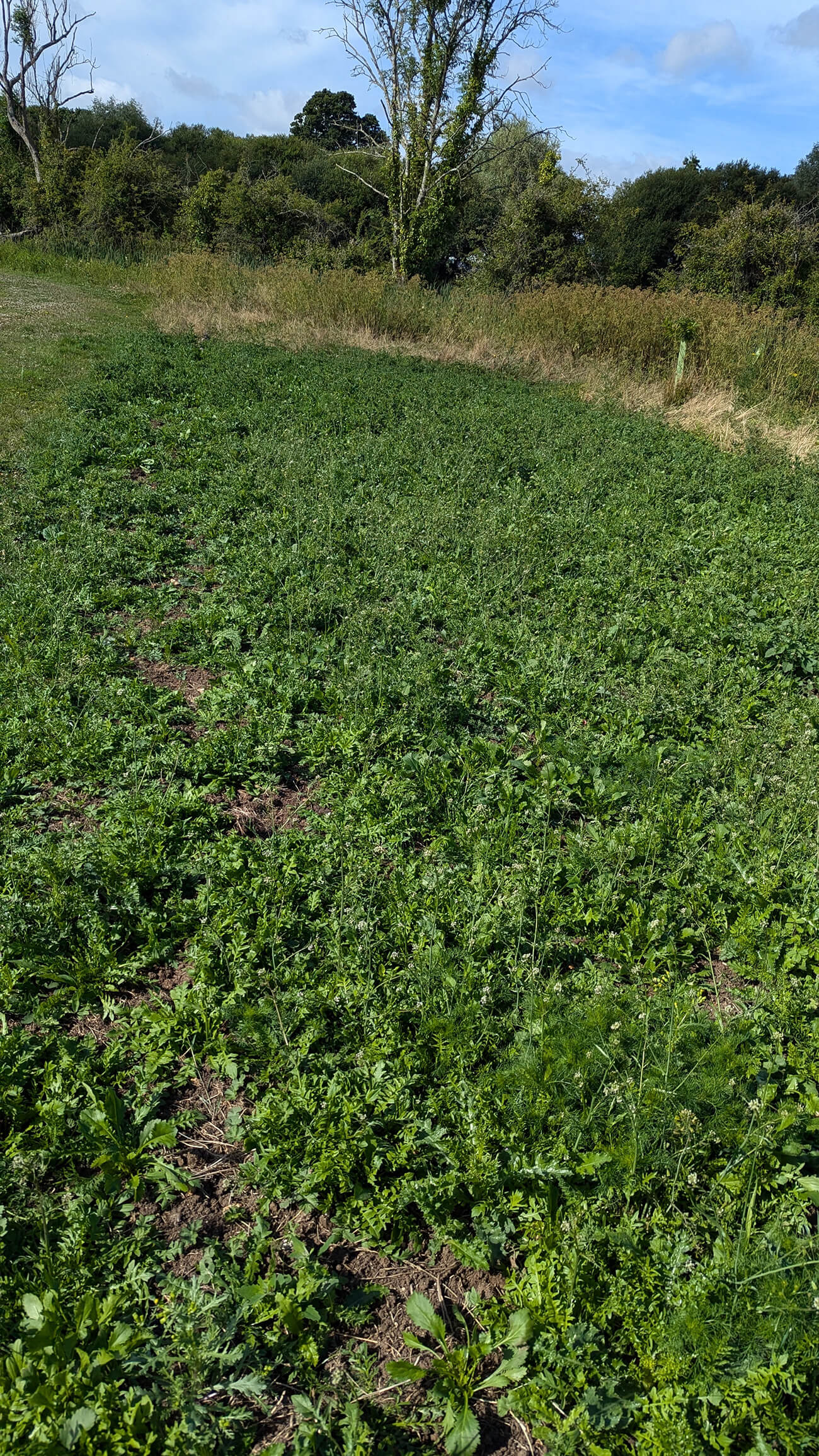
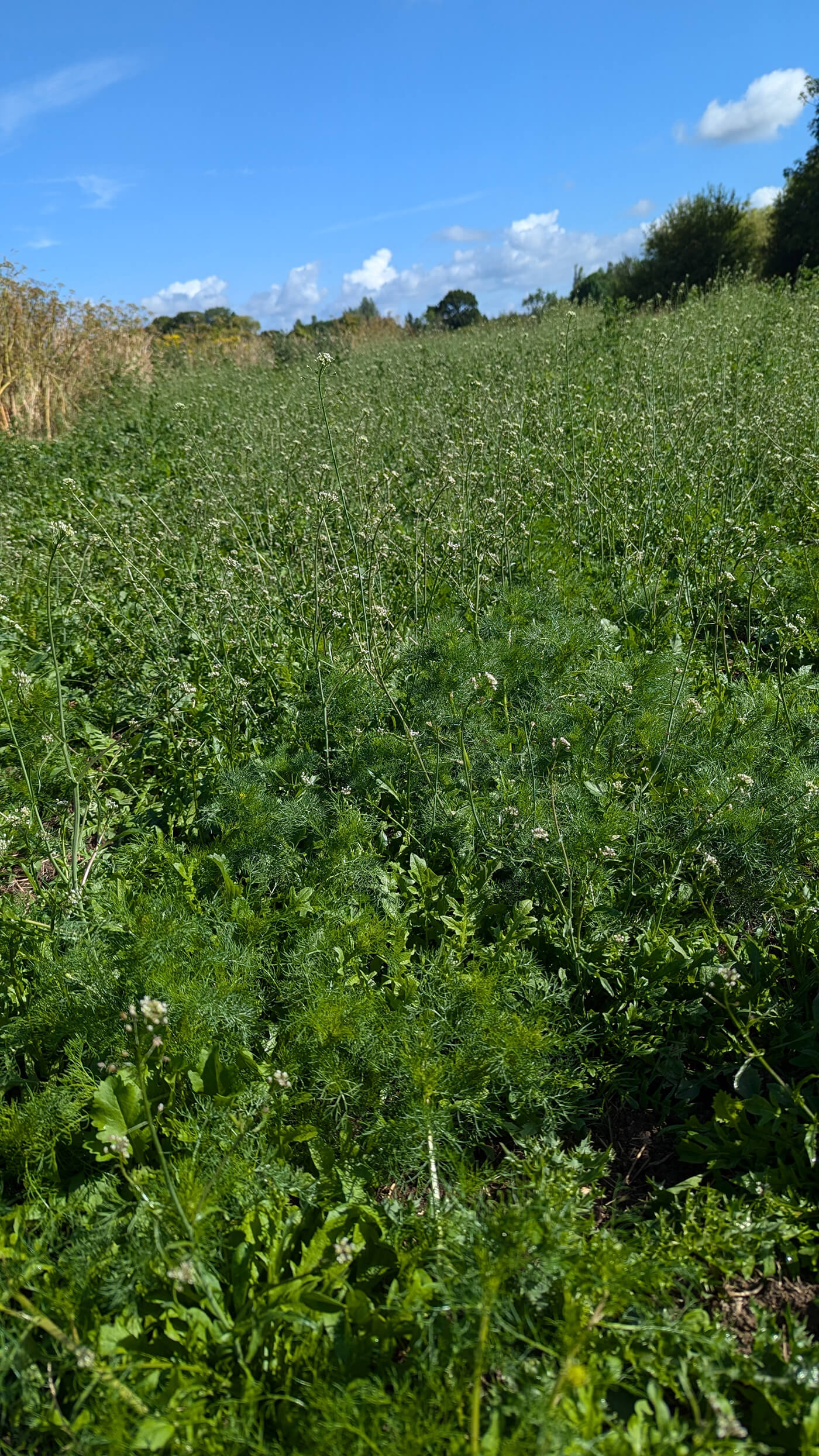
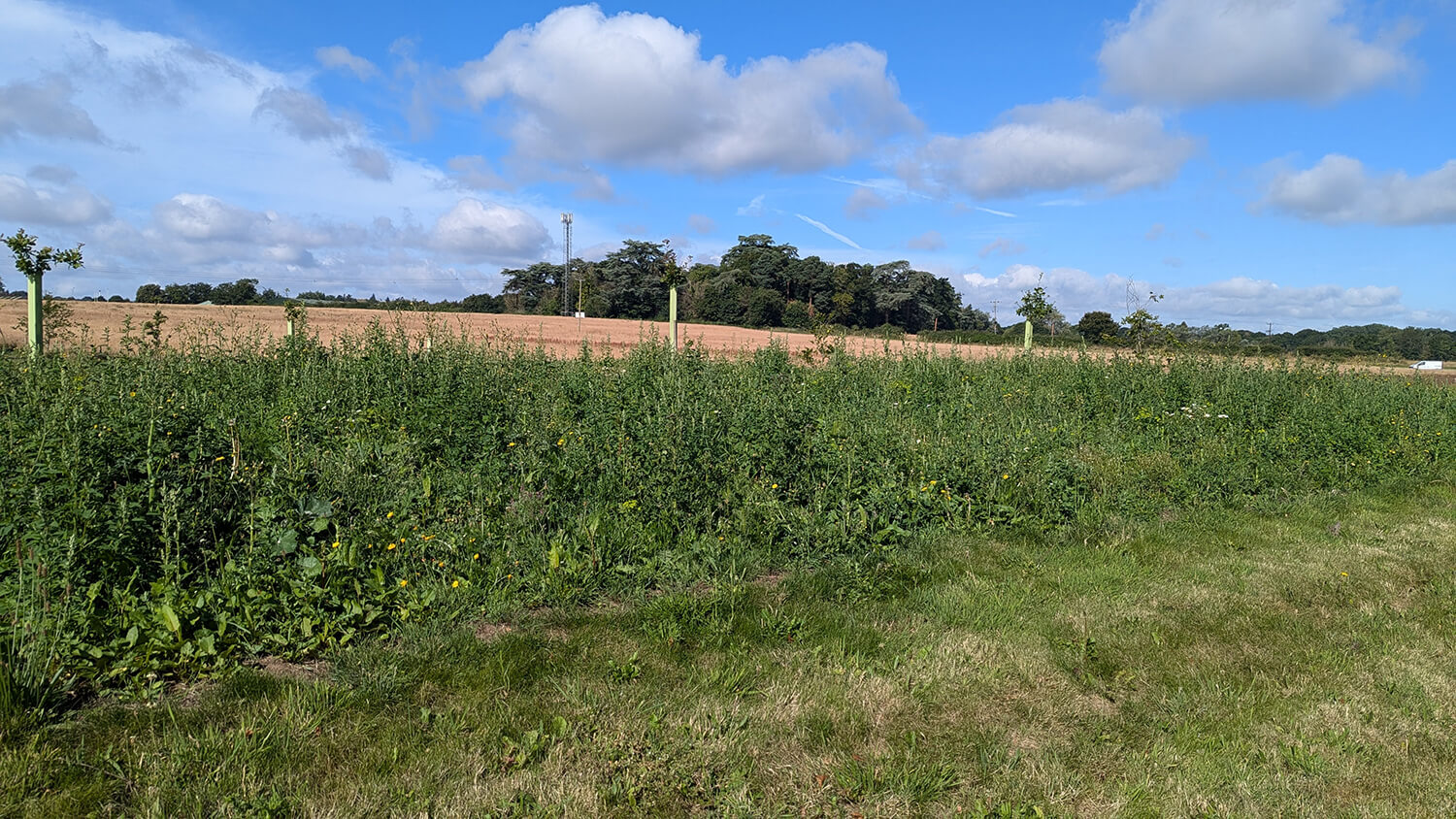
Wilflower restoration enhances plans of making this area an accessible and beautiful wildlife rich site for the local community to use, adding diverse habitat and an environment that better supports pollinators. The seed mix planted includes species Greater Knapweed, Wild Clary, Yarrow and Yellow Rattle to enhance the meadows on site and provide new habitat and forage for pollinating and other invertebrates.
The majority of the planting has been completed across the Autumn of 2023 and Spring of 2024, with some final seeding to take place in early Autumn 2024.
Grasses & Wildflowers Planted
UN's Sustainable Development Goals
As a GreenTheUK partner, you support projects that are in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.

Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.

Sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity loss.













































