Stadler Rail supported the planting of 1 hectare of wildflowers in the UK in 2025
Pollination underpins life on Earth, shaping ecosystems, global food production and the stability of the natural world we depend on every day. One out of every three mouthfuls of food relies on animal pollination, and in the UK alone the benefits that pollinators provide to crop production are estimated at £691 million each year. Yet despite their irreplaceable role, pollinators are in crisis. Scientific assessments show that pollinators are declining globally, driven by habitat loss, climate pressures and harmful chemicals. The health of our pollinating insects is directly tied to the security of our food systems and the resilience of natural ecosystems, which is why the support of organisations like Stadler Rail is so vital.
The UK hosts an exceptional variety of pollinating insects. There are 275 species of bee alone, alongside 280 hoverfly species, more than 2,200 moth species, 6,700 other species of fly, and numerous beetles, wasps and thrips that contribute to pollination. These species support not only our food crops but the wildflowers, grasslands and woodlands that underpin entire food chains.
The landscapes these species depend on have been dramatically altered. England and Wales have lost over 97% of its flower-rich grasslands since the 1930s, an area equivalent to one and a half times the size of Wales. These meadows once formed extensive, connected networks across the countryside; today, most survive only as isolated fragments. As a result, many pollinators struggle to find the nectar, pollen and nesting sites they need. This fragmentation is one of the primary reasons why once-widespread species have become rare or disappeared entirely.

The consequences of this loss are stark. Half of the UK’s 27 bumblebee species are in decline, three species have already gone extinct, and seven have suffered declines of more than 50% in just the last quarter-century. Our butterflies and moths tell the same story, with 71% of butterflies and two-thirds of moths now in long-term decline. Even common species are becoming increasingly scarce. The 2025 Bugs Matter Survey, led by Buglife and Kent Wildlife Trust, recorded a nearly 60% decrease in UK insect numbers since 2021, signalling severe and rapid ecological change.
This is why wildflower restoration is one of the most impactful interventions we can make. Wildflower-rich habitats support more pollinator species than any other habitat type, providing nectar, pollen, nesting opportunities and refuge throughout the year. GreenTheUK has partnered with Buglife to deliver the B-Lines initiative – a nationwide network of “insect highways” – to reconnect fragmented landscapes with new and restored wildflower areas, allowing pollinators to move, feed and breed across the country.
By supporting wildflower restoration with GreenTheUK and Buglife, Stadler Rail is helping to rebuild these ecological lifelines and reverse decades of habitat loss. This work extends far beyond protecting insects: it strengthens food security, enhances climate resilience, and restores the natural systems that future generations will depend on.
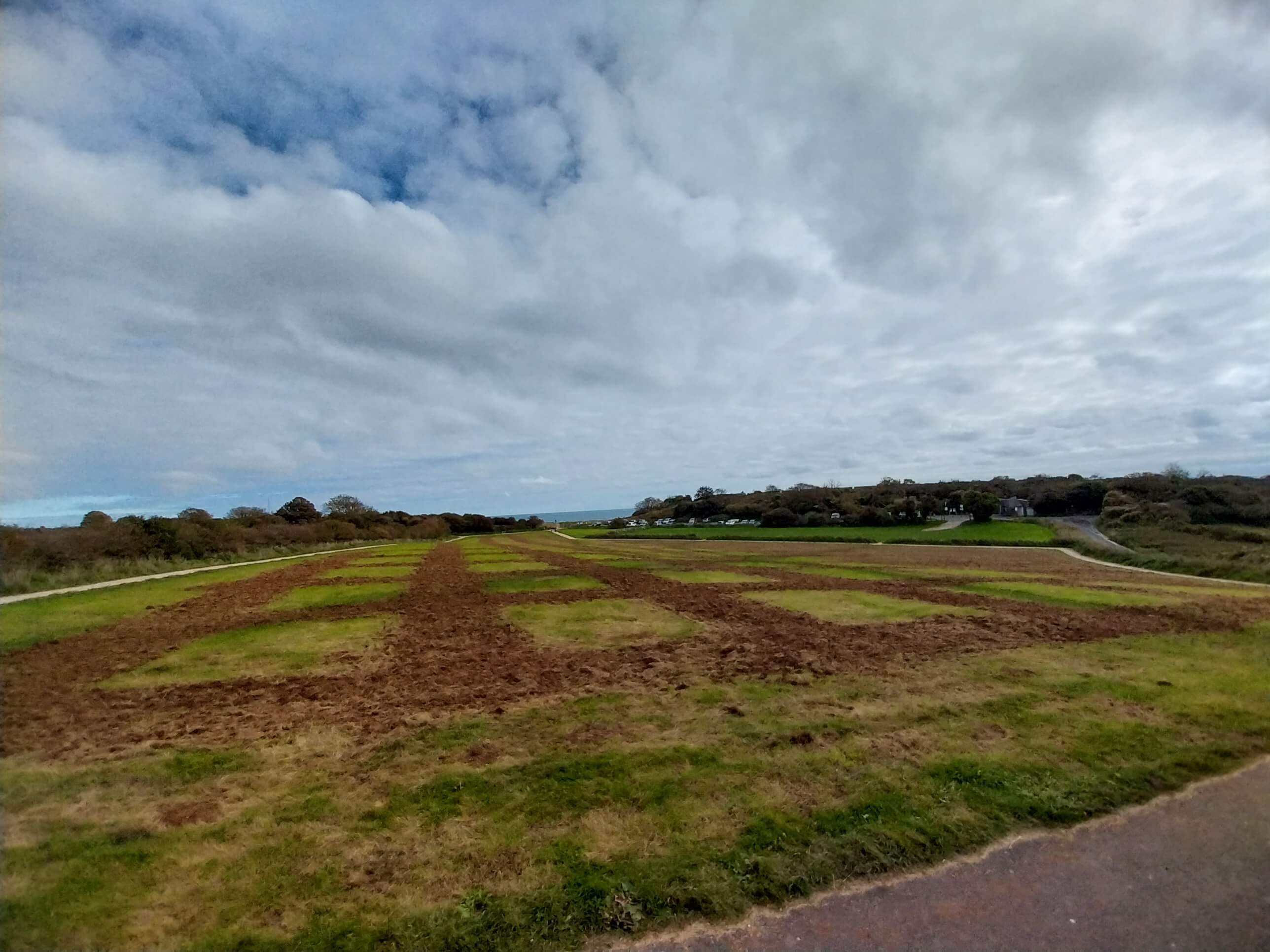
Wildflower Restoration in Devon (1 hectare)
Stadler Rail has supported important habitat restoration within Buglife’s Brownstone to Berry Head Hotspot, one of the five priority “Project Hotspots” within Life on the Edge - an ambitious partnership project working to restore viable populations of some of the UK’s rarest invertebrates and plants along the South Devon coast. This hotspot forms a crucial part of the South Devon coastal B-Line, where the project aims to restore or create over 675 hectares of species-rich grassland and reconnect fragmented habitats for at least thirty threatened invertebrate species.
The project site sits within the highly significant Berry Head National Nature Reserve, one of Torbay’s most treasured landscapes and a nationally important area for both biodiversity and heritage. The reserve carries multiple conservation and heritage designations, including Special Area of Conservation (SAC), Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI), and Scheduled Ancient Monument status. It is also home to the UK’s only Area of Special Protection, safeguarding the renowned guillemot colony by restricting boat access during the breeding season. Altogether, the reserve spans more than 170 acres of ecologically rich and historically important land, forming a cornerstone of the Life on the Edge project’s landscape-scale ambitions.
The restoration area, located beside the main car park, was previously low-diversity amenity grassland. To increase botanical richness and improve habitat quality, the sward was power-harrowed before wildflower seed was hand-broadcast and carefully trodden in. This sensitive, low-disturbance approach helps the seed establish effectively while respecting the ecological and cultural significance of this high-profile site - aligning with Life on the Edge’s commitment to targeted, high-quality habitat creation.
The resulting habitat improvements will benefit a wide range of specialist invertebrates recorded in the area, including the Goldilocks aster case-bearer moth (Coleophora artemisiella) and the orange-footed furrow bee (Lasioglossum xanthopus), both of which depend on diverse floral resources and well-connected grassland networks. By supporting this restoration work within such a nationally important landscape, Stadler Rail is contributing to the long-term conservation of rare species and helping strengthen biodiversity across one of South Devon’s most ecologically valuable hotspots.
Wildflowers & Grasses Planted
UN's Sustainable Development Goals
As a GreenTheUK partner, you support projects that are in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.

Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.

Sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity loss.